Site Search
Low-Code vs. No-Code: What’s the Difference and Which is Best for You?

Table of contents

Let's talk
Reach out, we'd love to hear from you!
Did you know that approximately 70% of new applications within an organization are expected to be built using low-code/no-code platforms by 2025?
The shift is happening, and businesses that ignore it are not only leaving money on the table but also compromising business growth and their ability to keep up with the competitive forces of the market.
Fundamentally speaking, both low-code and no-code (LCNC) development approaches aim to eliminate much of the complex aspects of coding with pre-configured, easier-to-use visual interfaces, templates, and elements. LCNC allows developers to create applications rapidly without getting lost in clunky code mechanics, complex syntax structures, and tedious debugging processes.
Both approaches shift the needle from “complicated” to “simplified” coding, making the entire development cycles:
- More efficient.
- More agile.
- More cost-effective.
And, with the recent advancements in data, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML), more and more intelligent features are getting amalgamated in software development processes across domains.
Low-Code and No-Code Development: Same, But Different
Back in the day, software development meant painstakingly typing every single line of code, while constantly referring to help pages or published journals to understand the nuances.
Then, came the era of IDEs—Integrated Development Environments—that brought us features like code editing automation, syntax highlighting, and smart debugging, cutting down a great deal of hassle and frustration for developers.
Fast forward to today, and we’re seeing the rise of low-code and no-code development where building software is as easy as dragging and dropping elements on the screen. Plus, developers have more time in hand to focus on solving complex problems instead of worrying about syntax or debugging!
Low-code and no-code systems focus on reducing and removing coding, respectively, suggesting that while they have some similarities, there are key differences that set them apart. In the next few minutes, we’ll take a closer look at:
- What is low-code development?
- What is no-code development?
- What are the key differences between low-code and low-code?
- What factors should businesses consider when choosing between low-code and no-code?
If you’ve ever felt confused about whether to go with low-code or no-code, you should bookmark this guide right away!
What is Low-Code Development?
Low-code can be described as a robust software development environment that allows users (without a developer’s intervention) to develop feature-rich software applications with minimal hand-coding. Such development processes are designed particularly for individuals having no coding experience.
Low-code development involves the use of intuitive interfaces powered by drag-and-drop components, code blocks, and pre-built templates, which instantly simplify the complex product engineering journey. In comparison to traditional coding methods, Low-code development paves the way for limitless possibilities, enabling businesses to take full advantage of a dynamic landscape brimming with key characteristics:
- Visual interfaces with pre-built templates with easy to use drag and drop features to create applications
- Swift application development and deployment while providing options for customization through manual coding when required
- Faster completion of routine aspects of coding tasks
- Built-in tools and functionality for rapid software development and maintenance, along with the flexibility and control
Low-code platforms allow versatility across a broad range of tasks, from automating repetitive development processes (giving your team valuable time back) to building complete websites or software applications. These platforms are widely embraced for creating web, mobile, and business solutions and are increasingly popular for automating workflows, modernizing legacy systems, and driving digital transformation.
Designed for both professional developers and “citizen developers”—business users with limited programming skills—low-code empowers them to easily create functional applications.
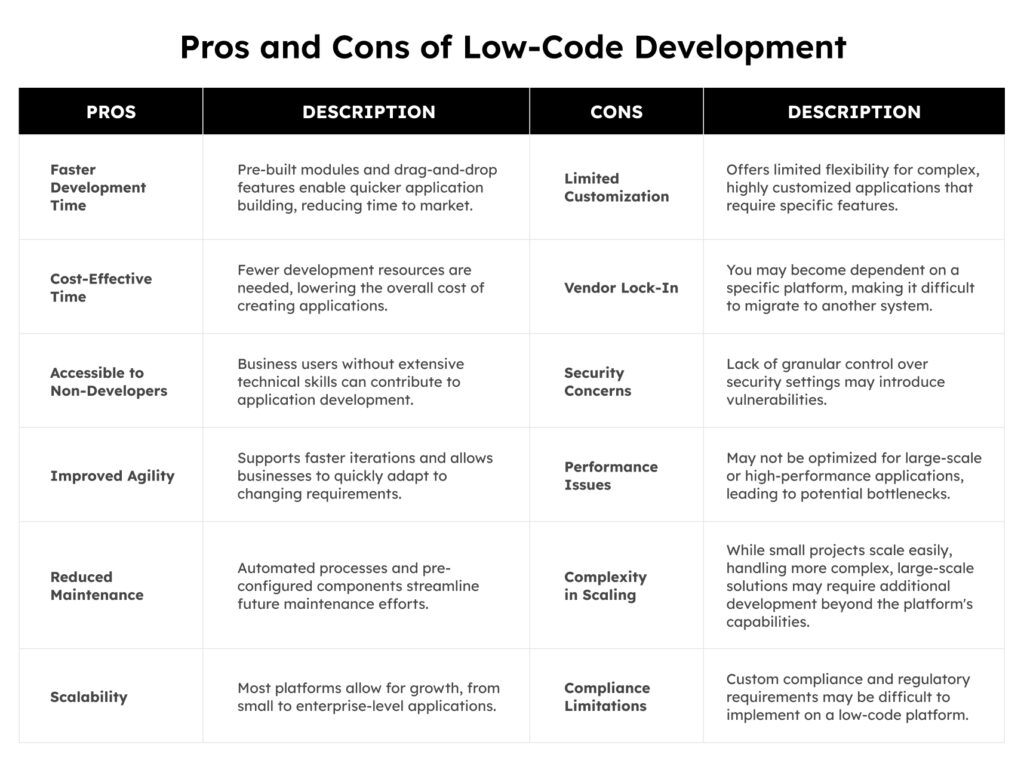
Pros and Cons of Low-Code Development
Low-code development has emerged as a popular solution for businesses seeking to accelerate application development while minimizing manual coding, but it comes with its own set of advantages and challenges that need careful consideration.

What is No-Code Development?
No-code application development allows users to build software applications with no coding required. This development technique offers a graphical user interface, making application development easy; any individual using this technique is often termed a citizen developer. This was created to be an easy-to-use tool that non-programmers and technically inexperienced people can use to build working applications.
No-code development is seeing the rise amongst non-technical business users to develop applications, and the growing sophistication rests peacefully on key characteristics:
- Uses graphical user interfaces with drag and drop functionalities
- Requires no previous programming language coding skills
- Highly interactive interfaces with predefined components to create websites, forms, and applications
- Enables swift development with and automation of processes
- Ideal for development of simple applications for individuals and small organizations
- May offer limited offer in terms of scalability or complex functionality
No-code platforms might actually be the future of application development compared to low-code, which is currently revolutionizing the application development dynamics with greater flexibility quotients across the business.
Pros and Cons of No-Code Development
No-code development doesn’t just minimize coding, but eliminates the need for it altogether. While this may paint a rosy picture, the approach comes with certain limitations, as discussed below.

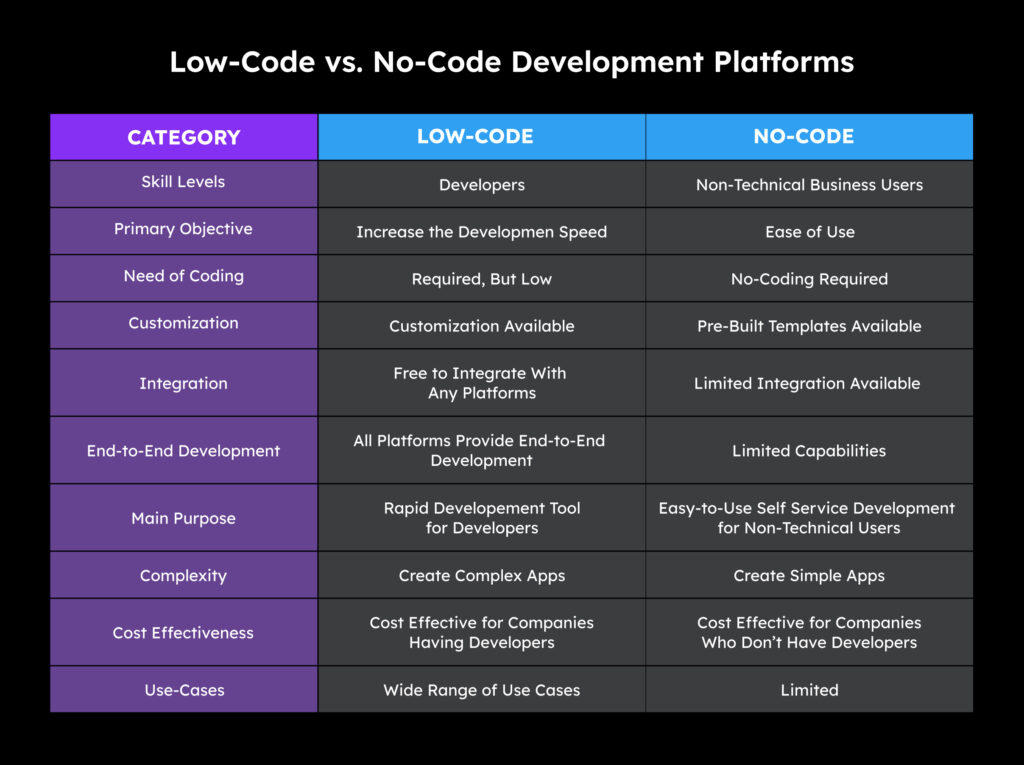
What are the Key Differences Between Low-Code and Low-Code?
For businesses, it’s important to understand the difference between low-code and no-code development, as each serves specific application needs.
For instance, one approach is designed for non-technical users with minimal coding experience, while the other is perfect for professional developers looking for more flexibility and customization to create powerful, intuitive applications tailored to specific business needs.
Let’s dive in and explore the key differences between Low-Code and No-Code development.
1. Skill Levels
- Low-Code: Designed for users with some programming knowledge. It allows developers to create applications using visual interfaces combined with some coding for advanced functionality. Best suited for professional developers or technically-savvy business users.
- No-Code: Requires no coding experience. Users can build applications purely through drag-and-drop interfaces, making it ideal for “citizen developers” who have little to no coding background, such as business analysts or managers.
2. Customization and Flexibility
- Low-Code: Offers more flexibility and customization since developers can add custom code. This makes it ideal for complex applications that need custom integrations, unique features, or specific business logic.
- No-Code: Limited customization options. Since no coding is involved, customization is generally confined to predefined templates and modules provided by the platform. This is best for simpler applications with standard functionality.
3. Primary Use Cases
- Low-Code: Suitable for both simple and complex applications, enterprise solutions, and large-scale systems that may need custom features or integration with existing IT infrastructure.
- No-Code: Ideal for quickly building smaller applications, MVPs (Minimum Viable Products), internal business apps, or simple workflow automations that don’t require extensive customization.
4. Target Users
- Low-Code: Geared towards professional developers or power users in IT who need to expedite development while retaining control over custom coding when necessary.
- No-Code: Aimed at business users or non-developers who need to build apps independently without IT or developer support, such as HR managers or marketers.
5. Speed of Development
- Low-Code: Faster than traditional development but may still involve some coding, especially for more advanced features.
- No-Code: Typically the fastest option, as it’s entirely visual, enabling quick app creation and deployment.
6. Application Complexity
- Low-Code: Suitable for a wide range of applications, from simple to highly complex, including enterprise-grade applications.
- No-Code: Typically used for simpler applications, as the lack of coding limits the ability to handle complex requirements.
7. Integration Capabilities
- Low-Code: Offers more extensive integration options, allowing developers to connect to external APIs, databases, and systems.
- No-Code: Limited integration capabilities, though many platforms include basic integrations with popular apps and services (e.g., CRM or ERP systems).
Low-Code vs. No-Code: Which is Right for You?
The decision comes down to your organization’s specific requirements and objectives as well as the technical capabilities of the team. If you need a heavily tailored application with lots of necessary functions and have access to developers who can work with coding, then low-code is for you.
On the same note, in scenarios where you require a fast way of creating basic applications without coding skills, no-code development will enable your non-technical users to implement their ideas and create value quite fast.
You should then identify whether your project needs are urgent, what resources you possess, and whether the solution will be sustainable in the long run.
When to Choose and When to Avoid
Both approaches come with their unique set of benefits that organizations can leverage in different business scenarios. However, it is crucial to understand when to choose low-code and when not to go ahead with no-code development as choosing the right approach will directly impact the speed up your digital transformation journey.
Let’s have a closer look at a breakdown of do’s and don’ts below:
What low-code development should ideally be used for?
- Complex Applications: Low-code is more suitable if the project comes down to a development of an application with specifications of a custom/complex nature, such as integrated workflows, third-party integration, or business-specific rules. Usually it provides a custom code solution in cases when visual components aren’t enough.
- Enterprise-Grade Systems: In cases where the system is big or for enterprise systems that have to seamlessly or securely connect with internal systems or databases, then low-code holds the key to the complexity required in building the applications.
- Technically Proficient Teams: Particularly when developers or IT staff are part of a team, low-code tools can enable developers to deliver solutions quicker but without loss of the ability to implement the bespoke code as necessary.
- Legacy System Modernization: If the objective is to bring in 21 st century functionality to legacy systems that have the capability to link into existing information technology architectures, then low-code tools provide superior connectivity features to enable this.
- Hybrid Needs: In cases where an aspect of the application can be built with ease while another complex, low code represents flexibility of the two extremes as one can employ visual development while also allowing custom code innovation when necessary.
When should you choose no-code development?
- Simple or MVP Applications: When it comes to the creation of a fast, basic application or MVP, no-code platforms are perfect. The platforms allow the rapid development of the application and are most suited for applications which do not have rigorous requirements.
- Business-Driven Applications: So, when end-users or “citizen developers” require developing in-house applications with minimal to no backing from professional developers, no-code is optimal. It allows users without programming knowledge to develop applications for particular sequences, information filling, project managing, or clients’ feedback.
- Rapid Prototyping: While prototyping or testing ideas no one has to code, no-code platforms provide the user with a functional prototype that can be adjusted at a faster rate compared to coding it from scratch.
- Limited IT Resources: It often makes sense if the organization has a small IT team or small development resources, departments can develop their apps through no-code, and avoid potential reliance on technical staff.
- Short-Term or Low-Complexity Projects: If you want to build an application that will not need constant updates, won’t have to be maintained for a long time, or needs particular customizations, then no-code is efficient and affordable.
Parting Thoughts
Businesses need to realize that low-code and no-code development aren’t just passing fads; they’re real game changers for innovation, flexibility, and efficiency.
These approaches are set to transform the software development landscape by lowering entry barriers, which will definitely speed up delivery. Plus, they empower diverse teams to create robust, interactive applications, completely changing how businesses innovate and adapt. So, are you ready to carve out your own path to better ideas, smarter decisions, and quicker development? Stop waiting and get started right now!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which is better: low-code or no-code?
The answer depends on your business requirements and the core expertise of your team. Low-code platforms are ideal for more complex applications where some coding skills are required to customize apps further. They are suited for professional developers and IT departments. On the other hand, No-Code platforms are designed for business users or non-technical teams, offering simple, drag-and-drop functionalities to build apps without writing any code.
What is low-code, no-code, and high-code?
Low-code, no-code, and high-code represent different levels of software development complexity. Low-code platforms combine visual tools with minimal coding, allowing developers to create complex applications faster while retaining some customization through code, whereas no-code platforms, by contrast, eliminate coding altogether, enabling non-technical users to build apps using drag-and-drop interfaces, ideal for simpler workflows. Lastly, high-code, or traditional coding, involves writing extensive manual code, offering full control over an application's functionality and scalability, making it suitable for more intricate projects.
Does no-code require skill?
Surprisingly, yes! While no coding is required, using no-code systems still demands an understanding of how apps should function. Users need skills in business logic, workflows, and general application design.
How does no-code development compare in terms of customization vs. low-code?
No-code platforms offer less customization compared to low-code. No-code platforms rely on pre-built templates and limited configurations, which means they’re best for simpler applications or specific use cases. Low-code platforms, on the other hand, allow developers to write some custom code, offering greater flexibility to handle complex workflows, integrate APIs, and scale applications.


